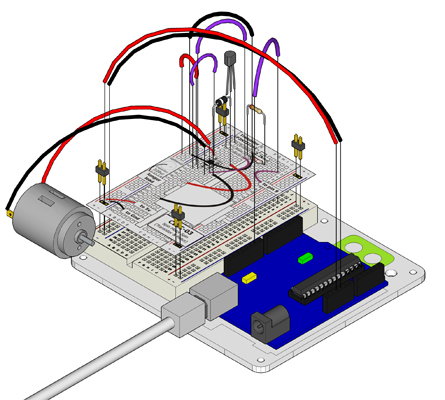
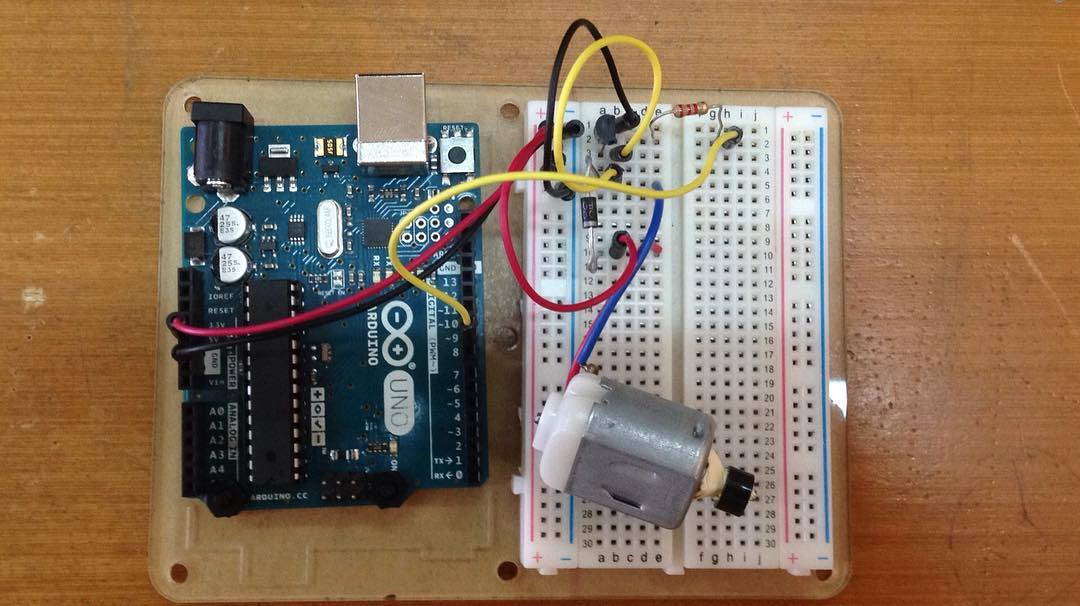
Apa yang kita lakukan
Pin arduino bisa mengendalikan benda elektronik kecil seperti LED. Tapi, ketika bermain dengan sesuatu yang lebih besar (seperti motor mainan atau mesin cuci), kita perlu transistor external. Transistor berguna untuk menyambung dan memutus arus besar dengan arus yang kecil. Sebuah transistor punya 3 pin. Untuk transistor negatif (NPN), kamu menghubungkan load ke connector dan emitter ke ground. Lalu ketika arus kecil mengalir dari base ke emitter, arus akan mengalir dari transistor dan motor akan hidup (ketika pin Arduino disetel sebagai HIGH). Ada banyak jenis transistor, yang memungkinkan setiap situasi punya solusi tersendiri. Kita menggunakan transistor P2N2222AG. Alasannya adalah karena maksimum voltage (40v) dan maksimum arus (200 mA) sudah cukup besar untuk motor kita. (lebih lanjut ada di datasheet http://ardx.org/2222)
Bahan bahan
 |
CIRC-03 Breadboard Sheet x1 |
 |
2 Pin Header x4 |
 |
Transistor P2N2222AG (TO92) x1 |
 |
Wire |
 |
Toy Motor x1 |
 |
Diode (1N4001) x1 |
 |
10k Ohm Resistor Brown-Black-Orange x1 |
 |
Rangkaian
Kode Program
/* -----------------------------------------------------------
* | Arduino Experimentation Kit Example Code |
* | CIRC-03 .: Spin Motor Spin :. (Transistor and Motor) |
* -----------------------------------------------------------
*
* The Arduinos pins are great for driving LEDs however if you hook
* up something that requires more power you will quickly break them.
* To control bigger items we need the help of a transistor.
* Here we will use a transistor to control a small toy motor
*
* http://tinyurl.com/d4wht7
*
*/
int motorPin = 9; // define the pin the motor is connected to
// (if you use pin 9,10,11 or 3you can also control speed)
/*
* setup() - this function runs once when you turn your Arduino on
* We set the motors pin to be an output (turning the pin high (+5v) or low (ground) (-))
* rather than an input (checking whether a pin is high or low)
*/
void setup()
{
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT);
}
/*
* loop() - this function will start after setup finishes and then repeat
* we call a function called motorOnThenOff()
*/
void loop() // run over and over again
{
motorOnThenOff();
//motorOnThenOffWithSpeed();
//motorAcceleration();
}
/*
* motorOnThenOff() - turns motor on then off
* (notice this code is identical to the code we used for
* the blinking LED)
*/
void motorOnThenOff(){
int onTime = 2500; //the number of milliseconds for the motor to turn on for
int offTime = 1000; //the number of milliseconds for the motor to turn off for
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH); // turns the motor On
delay(onTime); // waits for onTime milliseconds
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW); // turns the motor Off
delay(offTime); // waits for offTime milliseconds
}
/*
* motorOnThenOffWithSpeed() - turns motor on then off but uses speed values as well
* (notice this code is identical to the code we used for
* the blinking LED)
*/
void motorOnThenOffWithSpeed(){
int onSpeed = 200; // a number between 0 (stopped) and 255 (full speed)
int onTime = 2500; //the number of milliseconds for the motor to turn on for
int offSpeed = 50; // a number between 0 (stopped) and 255 (full speed)
int offTime = 1000; //the number of milliseconds for the motor to turn off for
analogWrite(motorPin, onSpeed); // turns the motor On
delay(onTime); // waits for onTime milliseconds
analogWrite(motorPin, offSpeed); // turns the motor Off
delay(offTime); // waits for offTime milliseconds
}
/*
* motorAcceleration() - accelerates the motor to full speed then
* back down to zero
*/
void motorAcceleration(){
int delayTime = 50; //milliseconds between each speed step
//Accelerates the motor
for(int i = 0; i < 256; i++){ //goes through each speed from 0 to 255 analogWrite(motorPin, i); //sets the new speed delay(delayTime); // waits for delayTime milliseconds } //Decelerates the motor for(int i = 255; i >= 0; i--){ //goes through each speed from 255 to 0
analogWrite(motorPin, i); //sets the new speed
delay(delayTime); // waits for delayTime milliseconds
}
}
Dokumentasi Video
Photo and video by kawan sekelompok -> Septian (Instagram)